Real-world examples of the use of satellite imagery data in agriculture
- By | August 02, 2021

Processing satellite imagery is essential for delivering actionable insights in the agriculture sector.
“How satellite imagery data is applied in agriculture” is a new use case guide published by Databroker, that provides an overview of the emerging use cases of geo-spatial satellite data in precision agriculture, environmental protection, subsidies, insurance and food security.
Let’s deep dive into some real-world examples.
Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is a farming management concept based on observing, measuring, and responding to inter and intra-field variability in crops. Satellite imagery supports precision agriculture by providing the needed data for more precise use of fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides, as well as optimizing the use and rotation of pastures, predicting yields and monitoring loss, to name a few.
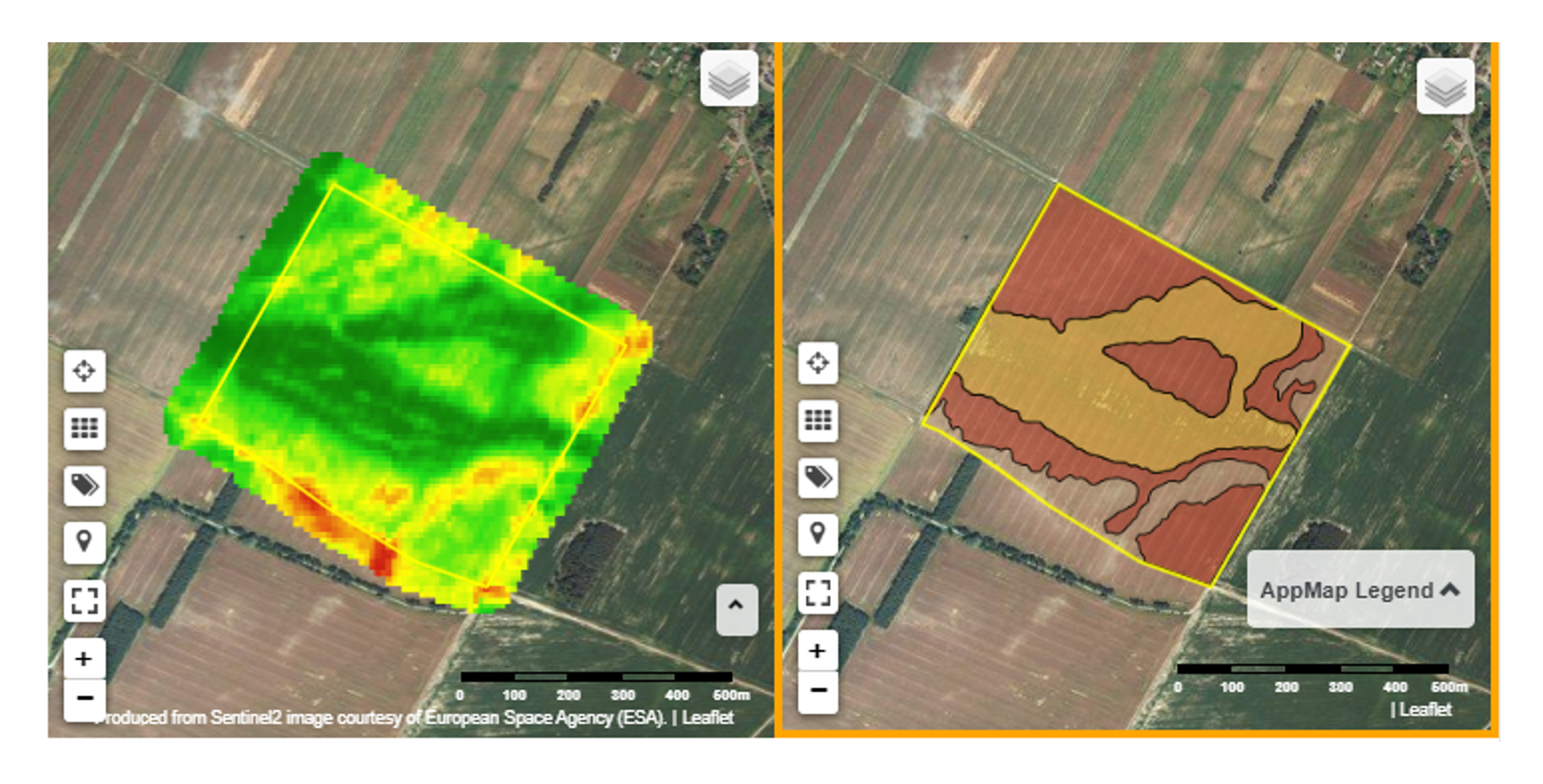
Polish startup SatAgro is an example of an agtech company that has been leveraging satellite imagery to enhance precision agriculture. According to the company, the variable-rate prescription maps generated from satellite images (and available within their app) have enabled farmers to cut the use of nitrogen fertilizer by 12 percent, thereby helping to maximize the potential of the land while minimizing environmental impact.
A screenshot from SatAgro’s app, showing farmers which areas within a field (red) to avoid applying fertilisers to (as doing so will have little effect on the yield anyway):
Food Security
Satellite imagery can be used to generate crop maps over large heterogeneous areas. In combination with census information, the crop maps can enable regional authorities to identify priority areas in need of assistance in the event of, for example, drought-related crop failures. This can inform planning that ultimately has the potential to reduce poverty, famine, and death.
NASA Harvest is an example of an initiative that has proven the efficacy of this model. Using satellite imagery from Sentinel-2, the NASA-USGS Landsat, and Planet’s SkySat, and subjecting it to machine learning algorithms, NASA Harvest was able to generate a cropland map within 10 days at the request of the Togolese Government. This map helped authorities to identify priority areas rapidly and effectively for its relief programs.
Would you like to know more about the growing potential and use cases of geo-spatial data in the agriculture sector?
Download the "How satellite imagery data is applied in agriculture" use-case guide here.














